Imagine: you sit down at your computer at 9:00. By 12:00, you feel as if your lower back has been replaced with a stone. Sounds familiar? It's not about age or "I just work too hard." It's about the chair.
When customers come to our showroom, the first thing they ask is:
"And which is better for your back - the one with the headrest and net, or the weird one that looks like a horse saddle?"
We don't give a formulaic answer. We ask counter-questions: How long do you sit? How often do you get up? Does your neck hurt after work? Because an "ergonomic chair" and a "saddle chair" are two completely different approaches.
Why do you even need an ergonomic chair?
We sit for an average of 9.3 hours a day — more than we sleep. According to a study by the British Journal of Sports Medicine , prolonged sitting increases the risk of cardiovascular disease by 147% and the likelihood of back pain almost doubles.
The most common consequences of incorrect sitting:
• Low back pain — 8 out of 10 people have experienced it in the last 6 months ( WHO data );
• Tension in the neck and shoulders (due to incorrect monitor and armrest height);
• Impaired blood circulation in the legs → heaviness, swelling, risk of varicose veins;
• Decreased productivity: according to Harvard Business Review , back pain reduces concentration by up to 40%.
An ergonomic chair is needed if:
• You work sitting for more than 4 hours a day;
• You feel discomfort in your back, neck, shoulders;
• Want to prevent muscle and spinal problems;
• Have an adjustable desk and want to alternate positions effectively.
And it's also an investment in your health: once you buy it, your body will thank you every day.
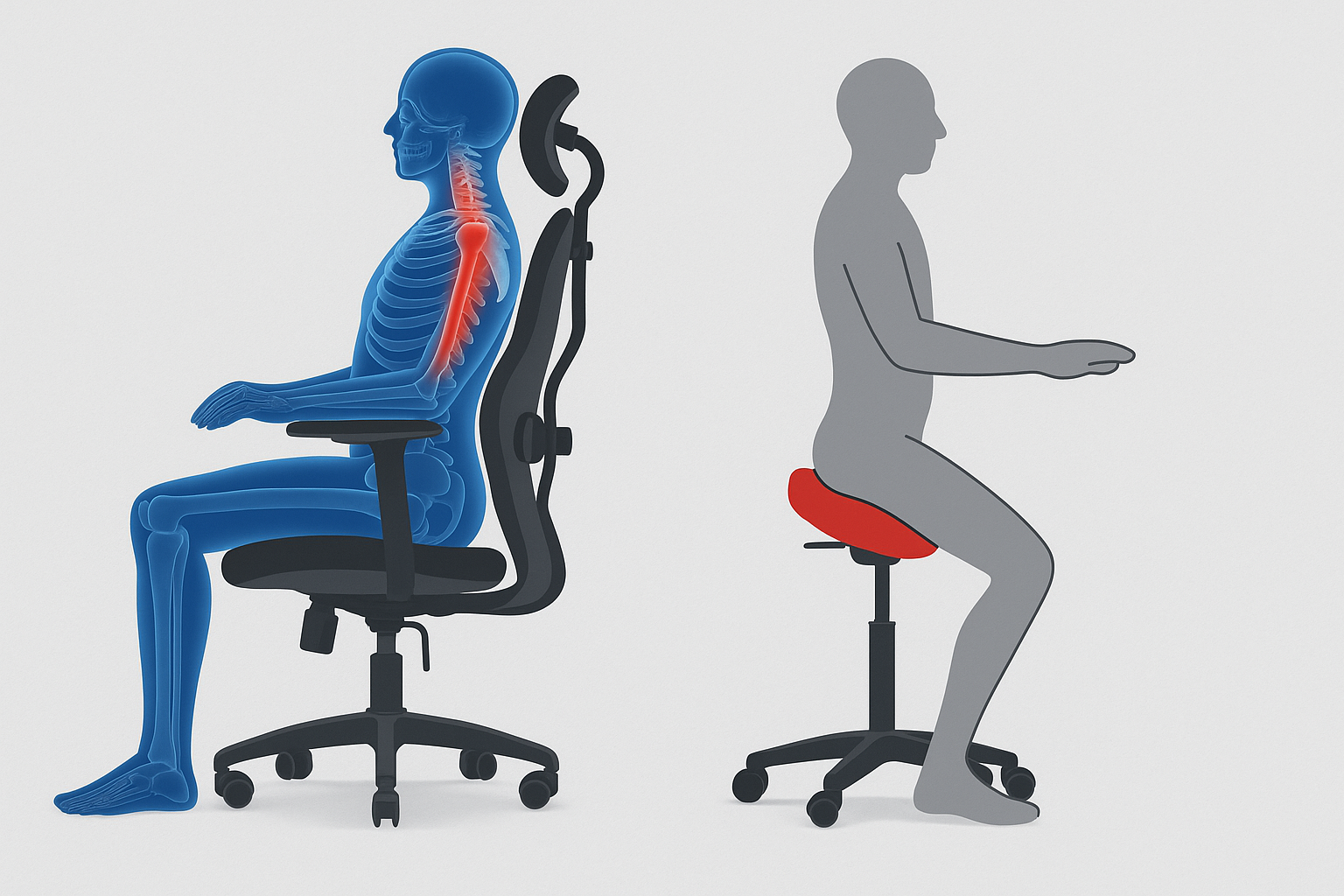
Ergonomic chair: personal comfort mode
It's like a nice car with a bunch of settings—if you know how to use them, the ride will be perfect. An ergonomic chair like the Contessa II or Ergohuman Elite 2 allows:
• adjust the seat height;
• adapt lumbar support;
• adjust the angle of inclination, depth, and armrests.
Users report a noticeable reduction in fatigue within the first week of use. But it's important to note that this chair allows you to "stick" — you sit comfortably, but your muscles don't work.
Saddle chair: active posture without effort
SALLI saddle chair SWAY is a leader in active seating solutions. Its shape aligns the spine, engages the stabilizer muscles, and forces the back to be naturally straight.
• Helps avoid compression load on the lower back;
• Activates blood circulation;
• Suitable for those who work in a dynamic environment or alternate sitting and standing.
Scientific research (see Spine Journal , 2021) confirm: sitting on a saddle chair significantly reduces pressure in the lumbar region compared to a classic chair, especially when sitting for more than 4 hours.
Comparison: ergonomic chair vs. saddle chair
|
Criterion |
Ergonomic chair |
Saddle chair |
|
Back support |
Passive (through the back) |
Active (muscles hold themselves) |
|
Comfort during prolonged sitting |
8+ hours |
2–3 hours (then it is worth alternating) |
|
Regulation |
Maximum possibilities |
Minimum (the body holds itself) |
|
Posture |
Depends on settings |
Always natural |
|
Adaptation |
Minimum |
3–7 days |
❗ Whatever chair you choose, there is a rule that always works: every 40–45 minutes you need to get up. Ideally, work standing for at least 10 minutes per hour. If there is no adjustable desk, do a little stretching, walk around the room, or do some inclines. Sitting is not harmful in itself - sitting without movement is harmful.

to share:
RockSolid dual-motor table: how to use and configure it correctly
A height-adjustable desk is a lifesaver for women's health: a comment from a gynecologist-endocrinologist